インストール単価(CPI)は、ユーザーがモバイルアプリをインストールするたびに広告主が広告ネットワークに支払う金額を表します。平均CPIは、総広告費で総インストール数を割ることで算出されます。
インストール単価(CPI)とは?
インストール単価(CPI)またはCPIは、モバイルアプリ広告の価格設定モデルで使用される主な指標の1つです。CPIは、ユーザーがモバイルアプリをインストールするたびに、広告主が広告ネットワークに支払う金額を表しています。これは設定された料金であり、通常、ユーザーが広告をクリックした後、初めてアプリをインストールして開いたときにのみ課金される。
CPIは、広告主が広告費のROIをより正確に追跡し、それに応じて広告を最適化できるため、アプリのインストールを促進する効果的な方法となり得ます。
CPIは、アドネットワークやパブリッシャー、ターゲットとするオーディエンス、アプリ市場における競合によって変化します。広告主は、最も関連性の高いオーディエンスに広告をターゲティングし、さまざまな広告クリエイティブをテストし、コンバージョン率を高めるためにアプリストアのリスティングを改善することで、CPIを最適化することができます。
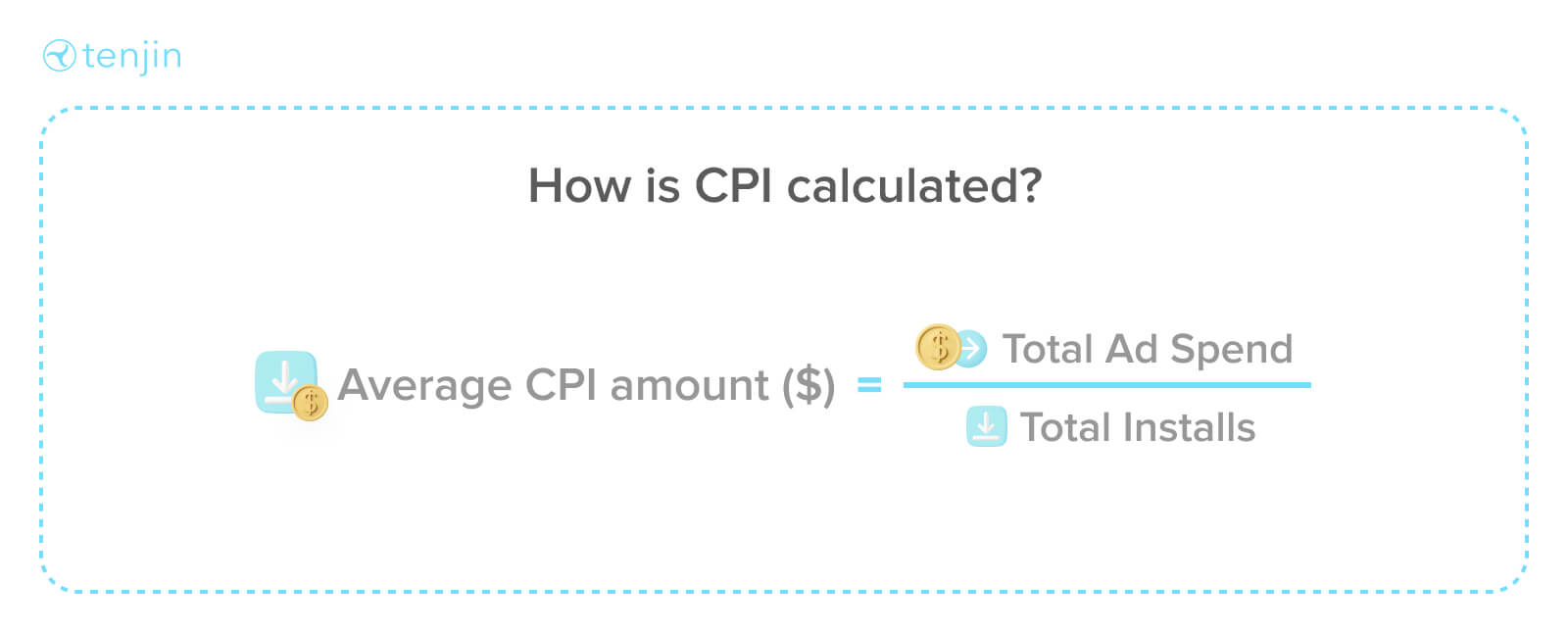
CPIの計算方法は?
平均CPI金額($)=総広告費/総インストール数
CPI = Total Ad Spend / Total Reported Installs
tCPI = Total Ad Spend / Total Tracked Installs
CPIが重要な理由は?
モバイルアプリの普及と成長を目指す企業やアプリ開発者にとって、CPIを積極的に測定することは重要です。その理由は以下の通りです:
-
費用対効果: CPIを測定することで、企業は新規アプリユーザーを獲得するための最も費用対効果の高い方法を判断することができます。CPIを追跡することで、企業はさまざまな広告キャンペーンやチャネルのパフォーマンスを評価し、CPIが最も低いものに集中することができます。
-
アプリの収益化: CPIはアプリが生み出す収益に直結します。CPIを追跡することで、企業は各アプリユーザーからどれだけの収益を上げれば収支が均衡するのか、あるいは望ましい利益率を達成できるのかを判断することができます。
-
アプリストアのランキング: アプリのインストール数は、アプリストアのランキングを決定する重要な要素です。CPIを追跡することで、企業はアプリのインストール数を増やすためにどの広告キャンペーンやチャネルが最も効果的かを判断し、アプリストアのランキングや知名度を向上させることができます。
-
ユーザーの継続: CPIを測定することで、企業はアプリのユーザーの質を評価することもできる。高いCPIで質の低いユーザーを獲得している場合、継続率が低くなり、全体的な収益が低下する可能性がある。CPIが低い質の高いユーザーの獲得に注力することで、企業はユーザー維持率を向上させ、長期的に収益を上げることができる。
CPIが良いかどうかを判断するには?
CPIは様々な要因(Android vs iOS、国、アプリのジャンルなど)に左右されます。Tenjinでは、アプリのCPIが良いかどうかを判断するために使用できるベンチマークレポートを定期的に公開しています。これらのレポートはこちらからご覧いただけます。